
🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
At Infinity Market Research, we dont just deliver data — we deliver clarity, confidence, and competitive edge.
In a world driven by insights, we help businesses unlock the infinite potential of informed decisions.
Here why global brands, startups, and decision-makers choose us:
Industry-Centric Expertise
With deep domain knowledge across sectors — from healthcare and technology to manufacturing and consumer goods — our team delivers insights that matter.
Custom Research, Not Cookie-Cutter Reports
Every business is unique, and so are its challenges. Thats why we tailor our research to your specific goals, offering solutions that are actionable, relevant, and reliable.
Data You Can Trust
Our research methodology is rigorous, transparent, and validated at every step. We believe in delivering not just numbers, but numbers that drive real impact.
Client-Centric Approach
Your success is our priority. From first contact to final delivery, our team is responsive, collaborative, and committed to your goals — because you re more than a client; you re a partner.
Recent Reports
Obesity Management Market
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market
Antisense Therapy Market
Antisense Therapy Market By Application (Genetic Disease, Cancer, Infectious Disease, Neurodegenerative Disorders, Cardiometabolic & Renal Disorders, Ocular Disorders, Respiratory Disorders, Skin Disorders, Others), By Route of Administration (Intravenous Injections, Intrathecal Injections), By Region and Companies)
Jun 2024
Healthcare
Pages: 129
ID: IMR1093
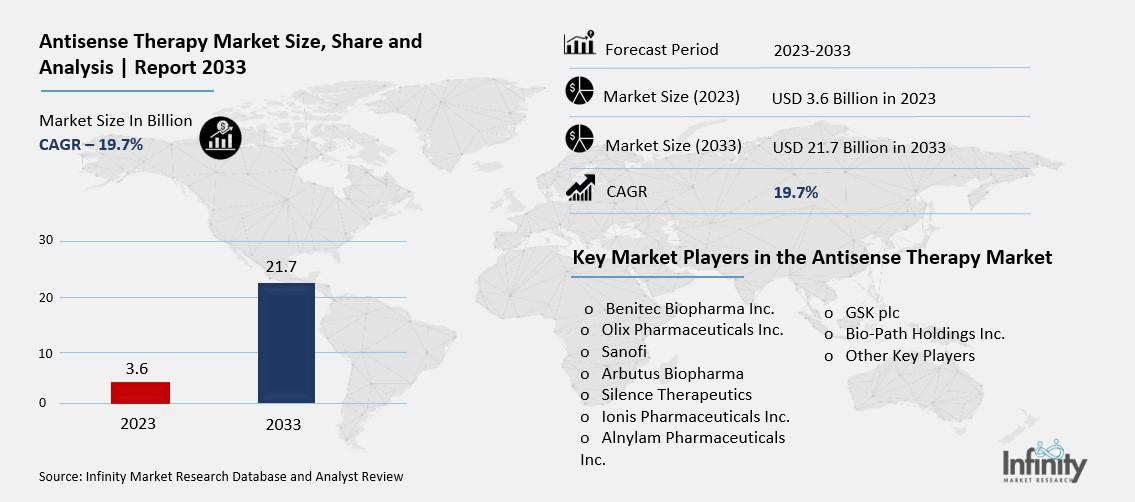
Antisense Therapy Market Overview
Global Antisense Therapy Market size is expected to be worth around USD 21.7 Billion by 2033 from USD 3.6 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 19.7% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
Antisense therapy is a medical treatment involving synthetic strands of nucleic acids, called antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), to target and inhibit the activity of specific genes. These synthetic strands are designed to bind to the messenger RNA (mRNA) produced by a particular gene, preventing the mRNA from being translated into a protein. By blocking the production of disease-causing proteins, antisense therapy can effectively treat various genetic disorders, cancers, and other conditions resulting from abnormal gene expression.
This approach is beneficial for diseases where faulty or overactive genes produce harmful proteins. For instance, in genetic disorders like spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), antisense therapy can target and correct the defective gene responsible for the disease, reducing symptoms and improving patient outcomes. The technology behind antisense therapy is also being explored for its potential to treat a wide range of conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancers.
Drivers for the Antisense Therapy Market
Advancements in Genetic Research:
Advancements in genetic research have significantly contributed to the growth of the antisense therapy market. Scientists are increasingly identifying disease-causing genes and developing antisense oligonucleotides that can target specific RNA sequences. This precision medicine approach allows for tailored treatments that address the underlying genetic causes of diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, and various types of cancers. As genetic research continues to evolve, the potential applications of antisense therapy are expanding, leading to a robust pipeline of therapeutic candidates.
Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases:
The rising prevalence of chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, is a major driver for the antisense therapy market. These diseases impose a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide, necessitating the development of innovative treatment options. Antisense therapy offers a targeted approach to treating these conditions by modulating gene expression or silencing disease-causing genes, thereby potentially halting disease progression and improving patient outcomes. The ability of antisense therapies to address unmet medical needs in chronic disease management is driving their adoption and market growth.
Demand for Personalized Medicine Solutions:
There is a growing demand for personalized medicine solutions that can provide targeted and effective treatments based on individual genetic profiles. Antisense therapy aligns with this demand by offering a personalized approach to treatment. By targeting specific RNA sequences or genetic mutations, antisense oligonucleotides can tailor treatment regimens to the genetic characteristics of each patient. This personalized approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes side effects, leading to better patient compliance and outcomes. As healthcare systems increasingly prioritize personalized medicine, the market for antisense therapy is expected to expand.
Technological Advancements in Drug Delivery:
Technological advancements in drug delivery systems have significantly improved the efficacy and safety profiles of antisense therapies. Innovations such as lipid nanoparticles, polymer conjugates, and viral vectors enable more efficient delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to target cells and tissues. These advancements help overcome biological barriers and reduce off-target effects, enhancing the therapeutic potential of antisense therapies. Additionally, the development of novel delivery systems allows for the delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to previously inaccessible tissues, expanding the scope of applications for antisense therapy in various disease areas.
Supportive Regulatory Environment:
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in the development and commercialization of antisense therapies. Regulatory agencies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of antisense therapies and adapting their frameworks to facilitate their approval and market access. Expedited review pathways and orphan drug designations for rare diseases are examples of regulatory incentives that support the development of antisense therapies. These supportive measures reduce development timelines and costs, encouraging investment in antisense therapy research and development.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Collaborations and partnerships between academia, pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology firms are driving innovation and advancing the antisense therapy field. These partnerships enable the pooling of resources, expertise, and capabilities to accelerate research, clinical development, and commercialization efforts. Collaborative efforts are particularly crucial in overcoming scientific challenges, such as optimizing drug delivery systems and identifying novel therapeutic targets. By leveraging complementary strengths, stakeholders in the antisense therapy market can expedite the translation of scientific discoveries into clinically meaningful treatments.
Restraints for the Antisense Therapy Market
Regulatory Challenges and Approval Hurdles
One of the major restraints in the antisense therapy market is the stringent regulatory environment. Governments and regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA require extensive clinical trials and safety data before approving new therapies. These processes are lengthy, costly, and require substantial investment in time and resources. This can delay the introduction of new antisense therapies to the market, potentially slowing down the overall growth of the sector. Companies often face significant hurdles in demonstrating the long-term efficacy and safety of their products, which can lead to delays or even rejection of approval applications.
High Cost of Development and Treatment
Developing antisense therapies involves high costs associated with research and development, clinical trials, and the production of complex molecules. The technology and expertise required are highly specialized, leading to increased costs. These expenses are often passed on to patients and healthcare providers, making treatments less accessible. The high cost of antisense therapies can limit their adoption, especially in low- and middle-income countries where healthcare budgets are more constrained. Additionally, insurers may be reluctant to cover these expensive treatments, further limiting patient access.
Delivery Challenges
Another significant restraint is the challenge of effectively delivering antisense molecules to the target cells. Antisense oligonucleotides are susceptible to degradation by nucleases in the bloodstream and face difficulties in crossing cell membranes to reach their intracellular targets. Despite advancements in delivery technologies such as nanoparticles and liposomes, ensuring the stability and bioavailability of antisense therapies remains a complex task. Inefficient delivery can reduce the effectiveness of the treatment and pose a barrier to wider adoption.
Market Competition and Intellectual Property Issues
The antisense therapy market is highly competitive, with numerous companies for a share of the market. This competition can be a restraint as companies must continually innovate and invest in new technologies to stay ahead. Intellectual property issues, such as patent disputes and the expiration of key patents, can also pose challenges. Companies may face legal battles over patent rights, which can be costly and time-consuming, diverting resources from product development and commercialization efforts.
Limited Awareness and Acceptance
There is still limited awareness and acceptance of antisense therapies among healthcare providers and patients. Many physicians may be more familiar with traditional treatment modalities and may hesitate to adopt newer, less established therapies. Additionally, there is a need for more education and evidence to convince the medical community of the benefits and safety of antisense treatments. Without widespread acceptance and understanding, the market growth of antisense therapies may be hindered.
Economic and Healthcare System Factors
Economic factors and the structure of healthcare systems can also restrain the market. In regions with less developed healthcare infrastructure, the adoption of advanced therapies like antisense treatments may be slower. Economic downturns and budget constraints can lead to reduced funding for new therapies and limited reimbursement options, impacting the market's growth potential. Additionally, healthcare systems that prioritize cost-effective treatments may be less likely to adopt higher-cost antisense therapies, even if they offer significant therapeutic benefits.
Opportunity in the Antisense Therapy Market
Antisense Therapy Market Expanding Horizons
The antisense therapy market is burgeoning with opportunities, driven by advancements in genetic research and the promise of personalized medicine. Antisense therapy involves using synthetic molecules called antisense oligonucleotides to target specific RNA sequences, thereby modulating gene expression and potentially treating a wide range of diseases, from genetic disorders to cancers.
Market Growth and Potential
The global antisense therapy market is on a trajectory of substantial growth. This growth is fueled by increasing investments in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors, alongside a rising demand for personalized medicine solutions. Antisense therapy offers a targeted approach, minimizing side effects and improving treatment efficacy, which further drives market adoption.
Applications Across Various Disease Categories
Antisense therapy has demonstrated promising results across diverse disease categories. In oncology, it is being explored for its potential to silence cancer-causing genes and inhibit tumor growth. For genetic disorders like Duchenne muscular dystrophy and cystic fibrosis, antisense oligonucleotides offer a mechanism to correct defective genes at the RNA level, potentially halting disease progression. Additionally, in infectious diseases such as COVID-19, antisense therapy can target viral RNA and inhibit viral replication, presenting a novel approach to combating emerging pathogens.
Challenges and Innovations in Delivery Systems
Despite its promise, antisense therapy faces challenges, primarily in the delivery of oligonucleotides to target cells and tissues. Researchers are actively developing innovative delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles and viral vectors, to enhance efficacy and minimize off-target effects. These advancements are crucial for overcoming biological barriers and improving the therapeutic potential of antisense therapies.
Clinical Trials and Collaborations
The field of antisense therapy is advancing rapidly through ongoing clinical trials and collaborations between academia, pharmaceutical companies, and biotech firms. These partnerships are essential for translating scientific discoveries into clinical applications and bringing new therapies to market. With a focus on safety, efficacy, and regulatory approval, these trials aim to validate the therapeutic potential of antisense therapies across a spectrum of diseases.
Future Prospects and Technological Integration
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in drug discovery and development processes holds promise for accelerating the identification of therapeutic targets and optimizing treatment outcomes. These technologies are expected to play a crucial role in the advancement of antisense therapy, facilitating personalized medicine approaches and expanding the therapeutic arsenal against complex diseases.
Trends for the Antisense Therapy Market
Emerging Trends in the Antisense Therapy Market
Antisense therapy is witnessing several emerging trends that are shaping its future, driven by advancements in genetic research, innovative drug delivery methods, and increasing applications across various disease categories.
Advancements in Genetic Research:
Recent advancements in genetic research have significantly expanded the scope of antisense therapy. Scientists are increasingly identifying new therapeutic targets at the genetic level, enabling the development of antisense oligonucleotides that can specifically target disease-causing genes. This precision allows for tailored treatments that address the underlying genetic causes of diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders, cancers, and rare genetic conditions. As genetic research continues to evolve, the potential applications of antisense therapy are expected to broaden, paving the way for personalized medicine solutions.
Innovative Drug Delivery Systems:
One of the key challenges in antisense therapy has been the efficient delivery of oligonucleotides to target cells and tissues. Recent innovations in drug delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles, polymer conjugates, and viral vectors, have significantly improved the efficacy and safety profiles of antisense therapies. These advancements enhance the ability of antisense oligonucleotides to penetrate cell membranes and reach their intended targets, while also reducing off-target effects. As these delivery systems continue to evolve, they are likely to further optimize the therapeutic potential of antisense therapies and broaden their clinical applications.
Expansion into Neurological Disorders:
There is growing interest in applying antisense therapy to neurological disorders, which represent a significant area of unmet medical need. Antisense oligonucleotides offer a promising approach for treating neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). By targeting specific genes associated with these conditions, antisense therapy aims to slow or halt disease progression, potentially improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of antisense therapies in neurological disorders, marking a pivotal moment in the field's development.
Rise in Oncology Applications:
Oncology remains a primary focus for antisense therapy, with numerous applications in cancer treatment. Antisense oligonucleotides can be designed to target oncogenes and inhibit tumor growth, offering a targeted approach with the potential for fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy. Recent advancements in understanding the genetic drivers of cancer have led to the development of novel antisense therapies that aim to personalize treatment regimens based on a patient's unique genetic profile. This personalized medicine approach holds promise for improving cancer treatment outcomes and reducing treatment-related toxicity.
Collaborative Efforts and Clinical Trials:
The antisense therapy landscape is characterized by extensive collaborative efforts between academia, pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology firms. These collaborations are essential for advancing research, conducting clinical trials, and translating scientific discoveries into clinical applications. By pooling resources and expertise, stakeholders in the antisense therapy market can accelerate the development of new therapies and navigate regulatory pathways more effectively. Ongoing clinical trials are critical for demonstrating the safety and efficacy of antisense therapies across different disease indications, further fueling market growth and innovation.
Regulatory Advancements and Market Expansion:
Regulatory agencies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of antisense therapies and adapting regulatory frameworks to facilitate their development and commercialization. This regulatory support, coupled with market demand for innovative therapeutic solutions, is expected to drive the expansion of the antisense therapy market. As more antisense therapies receive regulatory approval and enter the market, they have the potential to address significant unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes globally.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Application
o Genetic Disease
o Cancer
o Infectious Disease
o Neurodegenerative Disorders
o Cardiometabolic & Renal Disorders
o Ocular Disorders
o Respiratory Disorders
o Skin Disorders
o Others
By Route of Administration
o Intravenous Injections
o Intrathecal Injections
Segment Analysis
By Application Analysis
Antisense therapy is applied across a wide range of medical conditions, categorized into genetic diseases, cancer, infectious diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiometabolic and renal disorders, ocular disorders, respiratory disorders, skin disorders, and other miscellaneous conditions.
Genetic diseases are targeted using antisense therapy to correct or modulate genetic defects at the RNA level, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy and cystic fibrosis. In oncology, the therapy focuses on inhibiting cancer growth by targeting specific genes involved in tumor progression. Antisense therapy is also explored for infectious diseases like COVID-19, where it aims to inhibit viral replication by targeting viral RNA. Neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases are targeted to slow disease progression by addressing genetic factors.
Cardiometabolic and renal disorders utilize antisense therapy to target genes involved in metabolic processes or kidney function, such as hyperlipidemia and chronic kidney disease. Ocular disorders and respiratory disorders like inherited retinal diseases and cystic fibrosis are also treated using this therapy. Antisense therapy's diverse applications underscore its potential to address various unmet medical needs across different disease categories.
By Route of Administration
Antisense therapy is segmented by route of administration, including intravenous and intrathecal injections. The segment that generated the highest revenue was intrathecal injections, which involves injecting medicine into the subarachnoid space or spinal canal to reach the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This method is employed in pain management, spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, and the administration of drugs to treat specific infections, particularly following neurosurgical procedures.
Intrathecal injections are preferred for their direct delivery to the CSF, allowing medications to directly target the central nervous system. This route is crucial in neurological conditions where targeted therapy is essential, such as in managing pain or delivering chemotherapy agents directly to tumors in the central nervous system. The efficacy and safety of intrathecal injections make them a valuable option in clinical practice, ensuring precise and effective delivery of antisense therapies for various neurological and oncological indications.
Regional Analysis
North America: The market for antisense therapy in North America will be the largest because of the growing demand for effective treatments as medical expertise and diagnosis of specific disorders develop. The United States' research institutes and pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in the development of antisense medications, which will accelerate market expansion in this area. Additionally, strategic collaborations between academic institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and research organizations contribute to the region's dominance in the global market. The presence of key market players and high healthcare expenditure further supports the growth of antisense therapy in North America.
Europe: Europe is a significant market for antisense therapy, characterized by a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and advancements in genetic research. Countries such as the UK, Germany, and France are at the forefront of antisense therapy adoption, supported by robust healthcare infrastructure and strong regulatory frameworks. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) plays a crucial role in the approval and commercialization of antisense therapies, ensuring patient access to innovative treatment options. Ongoing clinical trials and research collaborations contribute to the region's expanding antisense therapy market.
Asia Pacific: The Asia Pacific region is emerging as a key market for antisense therapy, driven by a large patient pool, increasing healthcare expenditures, and rising demand for advanced therapeutic solutions. Countries like Japan, China, and Australia are witnessing significant growth in antisense therapy adoption, supported by advancements in biotechnology and genetic research. Moreover, government initiatives to promote precision medicine and support for innovative therapies contribute to market growth in the region. Collaborations between local biotech firms and international pharmaceutical companies further enhance the development and commercialization of antisense therapies in Asia Pacific.
Latin America: Latin America is experiencing gradual adoption of antisense therapy, supported by improving healthcare infrastructure and growing investments in biotechnology. Countries like Brazil and Mexico are leading the market, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and genetic disorders. Regulatory developments and clinical trials are crucial for expanding patient access to antisense therapies across the region. Collaboration between local and international stakeholders is key to overcoming healthcare challenges and driving market growth in Latin America.
Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa region are witnessing a nascent adoption of antisense therapy, characterized by a growing focus on precision medicine and genetic research. Countries like South Africa and the UAE are at the forefront of market growth, supported by improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing investments in biotechnology. Regulatory advancements and partnerships with international pharmaceutical companies are essential for accelerating the development and commercialization of antisense therapies in the region. Despite challenges, such as healthcare disparities and regulatory complexities, the market for antisense therapy in the Middle East and Africa shows promise for future growth.
Competitive Analysis
An extensive analysis of the market's major and up-and-coming players is provided by the Antisense Therapy Market Report. The report offers thorough lists of important businesses that have been selected based on the kinds of items they offer and other market variables. The researchers who worked on the study included the year of market entry for each participant listed, which can be taken into consideration for the research analysis of the business profiling market analysis.
Key Market Players in the Antisense Therapy Market
o Benitec Biopharma Inc.
o Olix Pharmaceuticals Inc.
o Sanofi
o Arbutus Biopharma
o Silence Therapeutics
o Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc.
o Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc.
o GSK plc
o Bio-Path Holdings Inc.
o Other Key Players
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size 2023 |
USD 3.6 Billion |
|
Market Size 2033 |
USD 21.7 Billion |
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
19.7% (2023-2033) |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Market Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
|
Historical Data |
- |
|
Market Forecast Units |
Value (USD Billion) |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
Application, Route of Administration, and Region |
|
Geographies Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World |
|
Countries Covered |
The U.S., Canada, Germany, France, U.K, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Brazil |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Benitec Biopharma Inc., Olix Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, Arbutus Biopharma, Silence Therapeutics, Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., GSK plc, Bio-Path Holdings Inc., and Other Key Players |
|
Key Market Opportunities |
Applications Across Various Disease Categories |
|
Key Market Dynamics |
Increasing Investment in Research and Development |
📘 Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much is the Antisense Therapy Market in 2023?
Answer: The Antisense Therapy Market size was valued at USD 3.6 Billion in 2023.
2. What would be the forecast period in the Antisense Therapy Market report?
Answer: The forecast period in the Antisense Therapy Market report is 2023-2033.
3. Who are the key players in the Antisense Therapy Market?
Answer: Benitec Biopharma Inc., Olix Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi, Arbutus Biopharma, Silence Therapeutics, Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., GSK plc, Bio-Path Holdings Inc., and Other Key Players
4. What is the growth rate of the Antisense Therapy Market?
Answer: Antisense Therapy Market is growing at a CAGR of 19.7% during the forecast period, from 2023 to 2033.

🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
- Accurate & Verified Data:Our insights are trusted by global brands and Fortune 500 companies.
- Complete Transparency:No hidden fees, locked content, or misleading claims — ever.
- 24/7 Analyst Support:Our expert team is always available to help you make smarter decisions.
- Instant Savings:Enjoy a flat $1000 OFF on every report.
- Fast & Reliable Delivery:Get your report delivered within 5 working days, guaranteed.
- Tailored Insights:Customized research that fits your industry and specific goals.



