
🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
At Infinity Market Research, we dont just deliver data — we deliver clarity, confidence, and competitive edge.
In a world driven by insights, we help businesses unlock the infinite potential of informed decisions.
Here why global brands, startups, and decision-makers choose us:
Industry-Centric Expertise
With deep domain knowledge across sectors — from healthcare and technology to manufacturing and consumer goods — our team delivers insights that matter.
Custom Research, Not Cookie-Cutter Reports
Every business is unique, and so are its challenges. Thats why we tailor our research to your specific goals, offering solutions that are actionable, relevant, and reliable.
Data You Can Trust
Our research methodology is rigorous, transparent, and validated at every step. We believe in delivering not just numbers, but numbers that drive real impact.
Client-Centric Approach
Your success is our priority. From first contact to final delivery, our team is responsive, collaborative, and committed to your goals — because you re more than a client; you re a partner.
Recent Reports
Obesity Management Market
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market
Car T-Cell Therapy Market
Car T-Cell Therapy Market (By Product (Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel), Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel), Carvykti (ciltacabtagene autoleucel), Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel), Tecartus (brexucabtagene autoleucel), Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel), Others Products), By Disease Indication (Leukemia, Lymphoma, Multiple Myeloma, Other Disease Indications), By End-Use (Hospitals and Cancer Treatment Centers), By Region and Companies)
Jun 2024
Healthcare
Pages: 101
ID: IMR1091
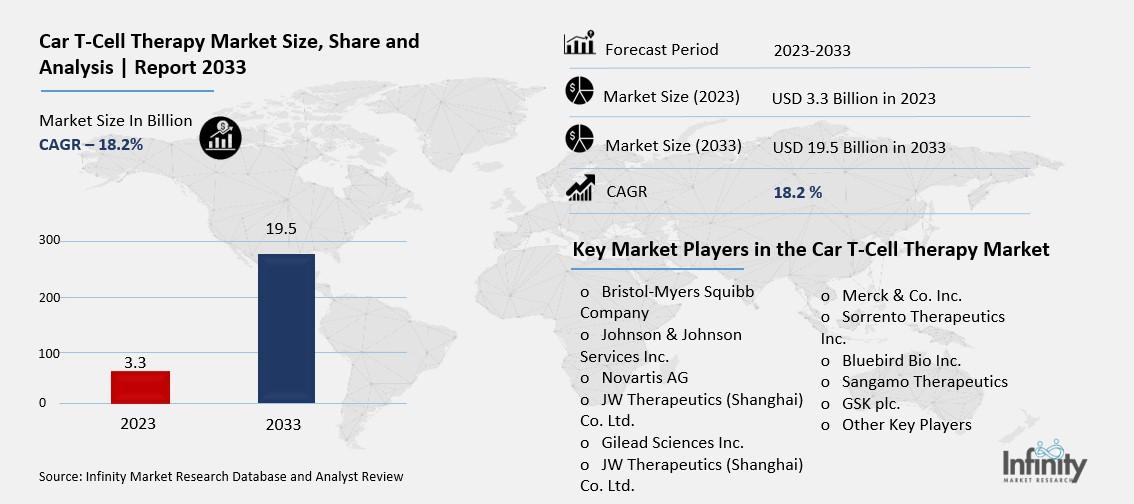
Car T-Cell Therapy Market Overview
Global Car T-Cell Therapy Market size is expected to be worth around USD 19.5 Billion by 2033 from USD 3.3 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 18.2% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
CAR T-cell therapy, short for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy, represents a groundbreaking approach to cancer treatment. It involves genetically modifying a patient's T-cells, a type of immune cell, to better recognize and destroy cancer cells. This therapy has shown remarkable efficacy in treating certain types of cancers that have been resistant to traditional treatments like chemotherapy or radiation.
The CAR T-cell therapy market encompasses a wide range of activities and industries. It includes the research and development efforts to refine and improve the therapy, the production of these specialized treatments, and the distribution networks that deliver them to patients. Moreover, clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing the therapy's application across different types of cancers and in various patient populations.
From a commercial perspective, the market involves pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions working together to bring these therapies from the lab to the clinic. The market growth is also driven by increasing investment in biotechnology research, the expanding number of clinical trials, and the approval of new therapies by regulatory agencies. As more research uncovers the potential of CAR T-cell therapy, it's anticipated that the market will continue to expand, offering new hope to patients with difficult-to-treat cancers.
Drivers for the Car T-Cell Therapy Market
Increasing Incidence of Cancer:
The rising incidence of cancer globally is a major driver for the CAR T-cell therapy market. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, accounting for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020. As the incidence of cancer continues to rise, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, there is a growing need for innovative and effective therapies like CAR T-cell therapy. This therapy has shown significant potential in treating hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma, which are among the most prevalent types of cancer.
Advancements in Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering:
Advancements in biotechnology and genetic engineering have significantly boosted the development and application of CAR T-cell therapies. Techniques for gene editing and cell engineering have become more sophisticated and accessible, allowing researchers to design CAR T-cells with enhanced specificity and potency against cancer cells. These technological advancements have accelerated the clinical development of CAR T-cell therapies and are expected to drive further innovation in the field.
Increasing Investment in Research and Development:
There is a substantial increase in investment in research and development (R&D) for CAR T-cell therapies. Pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions are actively investing in the development of new CAR T-cell therapies and the expansion of existing therapies into new indications. For example, in 2020, Novartis announced plans to invest $300 million to build a new facility for manufacturing CAR T-cell therapies. Such investments are crucial for advancing the clinical development and commercialization of CAR T-cell therapies.
Regulatory Approvals and Market Expansion:
The approval of CAR T-cell therapies by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has been a significant driver for market growth. In 2017, the FDA approved the first CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of certain types of leukemia and lymphoma, marking a milestone in cancer treatment. Subsequent approvals and expanded indications have further fueled market growth and increased patient access to these life-saving therapies.
Restraints for the Car T-Cell Therapy Market
High Cost of Therapy:
One of the primary restraints for the CAR T-cell therapy market is the high cost associated with these treatments. CAR T-cell therapies are complex and personalized treatments that involve the genetic engineering of a patient's immune cells. The manufacturing process is intricate and requires specialized facilities, which contributes significantly to the high cost. Treatment with CAR T-cell therapy can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars per patient. For example, in the United States, the list price for CAR T-cell therapies has been reported to range from $373,000 to $475,000 per treatment course. The high cost poses a significant financial burden on healthcare systems, insurers, and patients, limiting access to these therapies, especially in lower-income regions.
Challenges in Manufacturing and Logistics:
Another restraint for the CAR T-cell therapy market is the challenges associated with manufacturing and logistics. The production process for CAR T-cell therapies is complex and requires specialized infrastructure and expertise. The logistics of delivering these therapies to treatment centers and ensuring timely administration to patients also present significant challenges. Issues such as cell potency, stability during transport, and the need for stringent cryopreservation conditions add complexity and cost to the supply chain. Improvements in manufacturing efficiency and logistics infrastructure are needed to streamline production and reduce costs, thereby increasing accessibility and adoption of CAR T-cell therapies.
Risk of Adverse Events and Long-term Safety Concerns:
CAR T-cell therapy can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening side effects, known as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity. CRS is a systemic inflammatory response that can cause high fevers, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction. Neurotoxicity can lead to confusion, seizures, and other neurological complications. While these side effects are generally manageable with appropriate medical management, they pose risks to patients and require specialized monitoring and care. Additionally, the long-term safety of CAR T-cell therapies is still being studied, particularly regarding the potential for off-target effects and the persistence of engineered T-cells in the body. Addressing these safety concerns and improving the risk-benefit profile of CAR T-cell therapies are crucial for their broader adoption in clinical practice.
Market Competition and Patent Expirations:
The CAR T-cell therapy market faces competition from other emerging immunotherapy approaches, such as checkpoint inhibitors and other cell-based therapies. The expiration of key patents for first-generation CAR T-cell therapies could lead to increased competition from generic versions or biosimilars, potentially lowering prices but also impacting revenues for innovator companies. Moreover, the development of new and improved therapies by competitors could challenge the market position of existing CAR T-cell therapies. Continued innovation and differentiation will be essential for companies to maintain market leadership in this competitive landscape.
Opportunity in the Car T-Cell Therapy Market
Expanding Applications Across Different Cancer Types:
One of the primary opportunities for the CAR T-cell therapy market lies in expanding its applications across a broader range of cancer types. While initial approvals have focused on hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma, ongoing clinical trials are exploring the potential of CAR T-cell therapies in solid tumors. For example, CAR T-cell therapies targeting antigens like HER2, EGFR, and others are being investigated for breast cancer, lung cancer, and other solid tumors. According to the American Cancer Society, solid tumors account for approximately 90% of all cancer cases. If successful, the expansion into solid tumors could significantly broaden the market potential of CAR T-cell therapies and provide new treatment options for patients with challenging-to-treat cancers.
Advancements in CAR T-Cell Engineering and Technology:
Advancements in CAR T-cell engineering and technology present a substantial opportunity for the CAR T-cell therapy market. Researchers are continuously improving the design of CAR constructs to enhance efficacy, safety, and specificity against cancer cells. This includes the development of second-generation CARs with additional co-stimulatory domains, third-generation CARs with multiple co-stimulatory domains, and fourth-generation CARs (also known as TRUCKs) that incorporate cytokine expression to further stimulate immune responses. These advancements aim to improve the persistence and anti-tumor activity of CAR T-cells, potentially leading to better clinical outcomes and expanding the patient population that can benefit from these therapies.
Growing Investment in Clinical Research and Development:
There is a growing investment in clinical research and development (R&D) for CAR T-cell therapies, which represents a significant opportunity for market expansion. Pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions are investing heavily in advancing CAR T-cell therapies through clinical trials and regulatory approvals. For instance, as of 2023, there are over 1,000 ongoing clinical trials worldwide investigating CAR T-cell therapies for various cancers. These trials are exploring different targets, dosing regimens, and combination therapies to optimize treatment outcomes and expand the therapeutic potential of CAR T-cell therapies.
Patient Access and Healthcare Infrastructure Development:
Improving patient access to CAR T-cell therapies and developing healthcare infrastructure represent additional opportunities for market growth. Efforts are underway to establish specialized treatment centers capable of delivering CAR T-cell therapies and providing comprehensive care to patients. Healthcare systems are also working to streamline reimbursement processes and expand insurance coverage for these high-cost therapies, making them more accessible to patients who could benefit from them. Moreover, initiatives are focusing on building global manufacturing capabilities to meet the increasing demand for CAR T-cell therapies worldwide, potentially reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
Trends for the Car T-Cell Therapy Market
Personalized Medicine and Targeted Therapies:
A significant trend in the CAR T-cell therapy market is the shift towards personalized medicine and targeted therapies. CAR T-cell therapies are designed to be highly specific, targeting antigens expressed on the surface of cancer cells while sparing normal cells. This approach reduces the likelihood of off-target effects and improves the safety profile of the therapy. Advances in genomic profiling and biomarker identification are enabling the identification of specific patient populations who are most likely to benefit from CAR T-cell therapies. For example, CAR T-cell therapies targeting CD19 have shown promising results in patients with B-cell malignancies, leading to their approval for clinical use. The trend towards personalized medicine is expected to continue, with ongoing research focusing on identifying new targets and optimizing treatment protocols to improve patient outcomes.
Next-Generation CAR T-Cell Therapies:
Another trend in the CAR T-cell therapy market is the development of next-generation CAR T-cell therapies. These therapies aim to enhance the efficacy and durability of CAR T-cell responses against cancer. Second-generation CARs incorporate additional co-stimulatory domains such as CD28 or 4-1BB to improve T-cell activation and proliferation. Third-generation CARs further enhance T-cell function by incorporating multiple co-stimulatory domains. Fourth-generation CARs, or TRUCKs (T-cells redirected for universal cytokine killing), are engineered to secrete cytokines locally to enhance anti-tumor immunity. These advancements aim to overcome tumor resistance mechanisms and improve the persistence of CAR T-cells in the hostile tumor microenvironment. The development of next-generation CAR T-cell therapies is a major focus of ongoing research and clinical trials, with potential implications for expanding the therapeutic applications of CAR T-cell therapies.
Expansion into Solid Tumors:
There is a growing trend towards expanding the application of CAR T-cell therapies into solid tumors. While initial approvals have focused on hematologic malignancies, researchers are exploring CAR T-cell therapies targeting antigens such as HER2, EGFR, and others expressed on solid tumor cells. Clinical trials are evaluating the safety and efficacy of CAR T-cell therapies in various types of solid tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and pancreatic cancer. This trend reflects the increasing recognition of the potential of CAR T-cell therapies beyond hematologic malignancies and the demand for new treatment options for patients with solid tumors.
Collaboration and Partnerships:
Collaboration and partnerships between pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, academic institutions, and healthcare providers are emerging as a key trend in the CAR T-cell therapy market. These collaborations are aimed at advancing research and development efforts, optimizing manufacturing processes, expanding patient access, and navigating regulatory pathways. For example, partnerships between academic institutions and biotechnology companies have facilitated the translation of basic research into clinical applications, while collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers have focused on establishing specialized treatment centers capable of delivering CAR T-cell therapies. Such collaborations are essential for accelerating innovation and bringing new CAR T-cell therapies to market more efficiently.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Product
o Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel)
o Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel)
o Carvykti (ciltacabtagene autoleucel)
o Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel)
o Tecartus (brexucabtagene autoleucel)
o Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel)
o Other Products
By Disease Indication
o Leukemia
o Lymphoma
o Multiple Myeloma
o Other Disease Indications
By End-Use
o Hospitals
o Cancer Treatment Centers
Segment Analysis
By Product Analysis
In 2023, the Yescarta category accounted for 42.96% of the global market for CAR T-cell treatment. It is anticipated to increase at the quickest rate among all product segments over the projected period, Yescarta targets the CD19 antigen; it is sometimes referred to as axicabtagene ciloleucel. Yescarta is usually prescribed for large B-cell lymphoma in cases when at least two types of treatment for follicular lymphoma have failed, the cancer returns during the first year of treatment, or the first treatment does not work. The higher survival rates of individuals with relapsed large B-cell lymphoma are the reason for the substantial share. For example, according to Gilead 2022, the median event-free survival was four times higher than the current standard of therapy, and nearly twice as many patients (40.5%) who were receiving Yescarta survived for two years without experiencing any disease development.
By 2033, the CAR T-cell therapy market is anticipated to see significant growth in the Carvykti category. It is anticipated to expand between 2023 and 2033 at a CAGR of 16.17%. Carvykti is additional autologous immunotherapy used to identify and eliminate BCMA-expressing or B cell maturation antigen-expressing cells. Strong regulatory backing in the form of approvals and clinical trials has made it possible for cancer medication to develop rapidly. For example, the U.S. FDA authorized Ciltacabtagene autoleucel on February 28, 2022, indicating a broader use, particularly for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Furthermore, strong outcomes from clinical studies have been reported, with approximately 98% of research subjects responding to the treatment and 78% of subjects exhibiting no evidence of malignancy in their blood or bone marrow. The results demonstrated a solid foundation for cancer patients' therapy for a median of 22 months.
By Disease Indication Analysis
In terms of market share for CAR T-cell therapy, the lymphoma category accounted for 56.89% in 2023. Additionally, it is anticipated to grow the fastest across application segments. The existence of several CAR-T medications that specifically target lymphoma is responsible for the market share dominance. Tecartus, Yescarta, Breyanzi, and Kymirah, for instance, aid in the targeting of the CD-19 antigen, which helps eradicate big B-cell lymphoma in both adults and children. Additionally, CAR T-cell therapy can eradicate and lessen life-threatening diseases due to the high occurrence of lymphoma globally. According to Globocon 2020, there were over 544,000 new non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases worldwide in 2020, and there were almost 259,000 deaths associated with the disease.
By 2033, multiple myeloma is predicted to expand at the second-fastest rate in the market for CAR T-cell treatment. Its projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is 21.95% from 2023 to 2033. Multiple myeloma has become more commonplace worldwide. According to a Lancet Hematology 2020 analysis, the age-standardized multiple myeloma rate was 1.78 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. The study showed a sharp rise in the overall incidence from nations with comparatively high rates of men 50 years of age or older. The FDA in the United States is still in favor of product approvals for CAR T therapy medications, which will lower the death rate among multiple myeloma patients. For example, the U.S. FDA authorized idecabtagene violence, also known as Abecma, in April 2021 for the treatment of multiple myeloma in patients who have not responded to previous cancer treatments or in cases where the disease has returned after four different rounds of treatment.
By End-Use Analysis
In terms of market share, hospitals accounted for 55.95% of the CAR T-cell therapy market in 2023. Strong technology, well-equipped operating rooms such as theaters, and large purchasing power for hospitals in key regions are the reasons for the market share dominance. Additionally, by utilizing their own CAR T process, hospitals can lower the total cost associated with the therapy, increasing their investment in these spaces. For example, Sheba Hospital in Israel uses internal procedures relevant to the procedure, which cuts treatment times to less than 10 days total and significantly lowers expenditures by at least 50%. According to the business website, since 2015, the hospital has treated close to 250 patients with CAR T therapy, drawing patients from across the globe.
By 2033, the CAR T-cell therapy market is predicted to have its fastest-growing segment: cancer treatment centers. Its projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is 25.89% from 2023 to 2033. This is because there are numerous therapy alternatives and patient comfort measures available. Furthermore, patients receive care in their local communities, broadening the scope of CAR T treatment. Finally, prestigious administrative institutions' strategic measures will improve patient coverage. For example, the UVM Cancer Center in Vermont, USA, stated in February 2023 that a novel CAR T-cell treatment was now available for patients with blood cancer.
Regional Analysis
In 2023, North America held the largest market share and generated around 65.90% of the total revenue in the CAR T-cell therapy business. The region's strong position is made possible by the presence of large corporations, increased government financing, research activity, and robust insurance coverage. Since the typical cost of CAR-T therapies is USD 400,000 or more, robust insurance plans ensure patient comfort and market expansion.
The U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, for example, declared in August 2019 that CAR T-cell therapy will be covered. With the relocation, a wider range of the region's senior population—whose incidence of blood cancer is high—can be definitively covered. According to the Federation of American Scientists 2023, 18.2% of all Americans, or around 60 million individuals are enrolled in Medicare.
The CAR T-cell treatment sector is expected to grow at the fastest pace in Asia-Pacific by 2033. Its projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is 26.74% from 2023 to 2033. The region's expanding patient base and legal backing for the products and industry participants are the reasons for the rapid expansion. Additionally, the market's expansion is being aided by the key players' increased attempts to produce technologically sophisticated medicines. For example, according to the Clinical Trials Database 2023, approximately 103 CAR T therapies are undergoing active clinical phases in China, and approximately 5 CAR T therapy studies are being developed in Australia.
Competitive Analysis
Major players have a lot of potential to profit from the strong demand for CAR T-cell therapy in treating blood cancers that have relapsed or distorted. Prominent entities are implementing many tactics, including partnerships, mergers, expansions, and acquisitions, to enhance their market share and fortify their market standing. For example, Ginkgo Bioworks and the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation (WARF) partnered in April 2023 to create the next generation of GD2 CAR T-cell therapies.
Key Market Players in the Car T-Cell Therapy Market
o Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
o Johnson & Johnson Services Inc.
o Novartis AG
o JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
o JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
o Merck & Co. Inc.
o Sangamo Therapeutics
o GSK plc.
o Other Key Players
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size 2023 |
USD 19.5 Billion |
|
Market Size 2033 |
USD 3.3 Billion |
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
18.2% (2023-2033) |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Market Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
|
Historical Data |
- |
|
Market Forecast Units |
Value (USD Billion) |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
Product, Disease Indication, End-Use, and Region |
|
Geographies Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World |
|
Countries Covered |
The U.S., Canada, Germany, France, U.K, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Brazil |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc., Novartis AG, JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Gilead Sciences Inc., JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Merck & Co. Inc., Sorrento Therapeutics Inc., Bluebird Bio Inc., Sangamo Therapeutics, GSK plc., Other Key Players, |
|
Key Market Opportunities |
Expanding Applications Across Different Cancer Types |
|
Key Market Dynamics |
Increasing Incidence of Cancer |
📘 Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much is the Car T-Cell Therapy Market in 2023?
Answer: The Car T-Cell Therapy Market size was valued at USD 3.3 Billion in 2023.
2. What would be the forecast period in the Car T-Cell Therapy Market?
Answer: The forecast period in the Car T-Cell Therapy Market report is 2023-2033.
3. Who are the key players in the Car T-Cell Therapy Market?
Answer: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc., Novartis AG, JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Gilead Sciences Inc., JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Merck & Co. Inc., Sorrento Therapeutics Inc., Bluebird Bio Inc., Sangamo Therapeutics, GSK plc., Other Key Players,
4. What is the growth rate of the Car T-Cell Therapy Market?
Answer: Car T-Cell Therapy Market is growing at a CAGR of 18.2% during the forecast period, from 2023 to 2033.

🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
- Accurate & Verified Data:Our insights are trusted by global brands and Fortune 500 companies.
- Complete Transparency:No hidden fees, locked content, or misleading claims — ever.
- 24/7 Analyst Support:Our expert team is always available to help you make smarter decisions.
- Instant Savings:Enjoy a flat $1000 OFF on every report.
- Fast & Reliable Delivery:Get your report delivered within 5 working days, guaranteed.
- Tailored Insights:Customized research that fits your industry and specific goals.



