
🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
At Infinity Market Research, we dont just deliver data — we deliver clarity, confidence, and competitive edge.
In a world driven by insights, we help businesses unlock the infinite potential of informed decisions.
Here why global brands, startups, and decision-makers choose us:
Industry-Centric Expertise
With deep domain knowledge across sectors — from healthcare and technology to manufacturing and consumer goods — our team delivers insights that matter.
Custom Research, Not Cookie-Cutter Reports
Every business is unique, and so are its challenges. Thats why we tailor our research to your specific goals, offering solutions that are actionable, relevant, and reliable.
Data You Can Trust
Our research methodology is rigorous, transparent, and validated at every step. We believe in delivering not just numbers, but numbers that drive real impact.
Client-Centric Approach
Your success is our priority. From first contact to final delivery, our team is responsive, collaborative, and committed to your goals — because you re more than a client; you re a partner.
Recent Reports
Obesity Management Market
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market (By Technology (LNG FPSO, FSRU, Others), By Capacity (Small/Mid-Scale, Large Scale, Others), By End-Use (Power Generation, Industrial, Others), By Region and Companies)
Aug 2024
Energy and Power
Pages: 138
ID: IMR1193
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market Overview
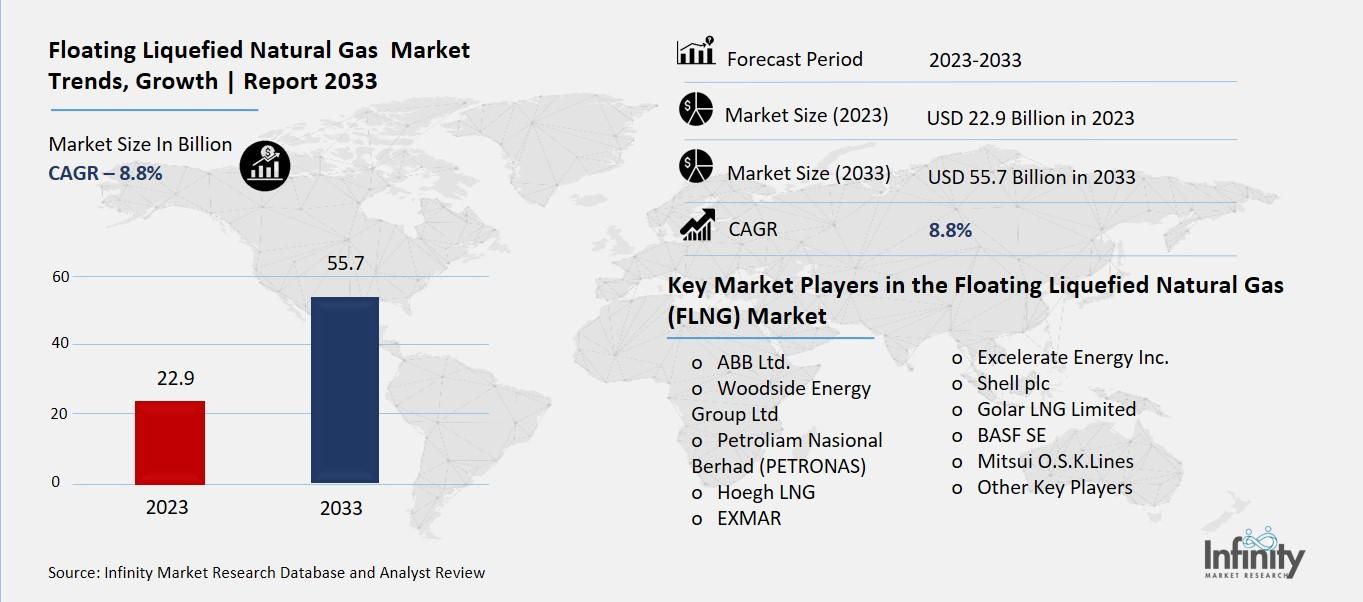
Global Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market size is expected to be worth around USD 55.7 Billion by 2033 from USD 22.9 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
The Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) market revolves around a unique and innovative technology used to extract and process natural gas at sea. Instead of building costly and complex onshore facilities, FLNG units are floating structures that can extract, liquefy, and store natural gas directly on the ocean. This approach allows for more efficient exploitation of offshore gas fields, especially those located far from land. These floating units can move to different locations, making them highly versatile and a cost-effective solution for tapping into remote gas reserves.
FLNG technology is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to reduce the environmental impact and logistical challenges associated with traditional onshore gas processing facilities. By processing the gas directly at sea, FLNG units minimize the need for long pipelines and extensive infrastructure, leading to lower emissions and a smaller footprint. As the demand for cleaner energy sources like natural gas continues to grow, the FLNG market is set to expand, offering a promising alternative to conventional gas extraction and processing methods.
Drivers for the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market
Increasing Demand for Natural Gas
The demand for natural gas is on the rise globally, driven by its reputation as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil. As countries seek to reduce carbon emissions and meet environmental regulations, natural gas becomes an attractive option. FLNG technology enables the extraction of gas from remote offshore locations, making it accessible and viable for markets with limited onshore infrastructure. This growing need for cleaner energy sources significantly drives the FLNG market, offering a sustainable and efficient solution for energy production.
Cost Efficiency and Flexibility
FLNG projects offer substantial cost advantages over traditional onshore liquefaction facilities. The ability to eliminate the need for extensive onshore infrastructure reduces capital expenditure. Additionally, FLNG units can be relocated to different gas fields, providing operational flexibility and allowing companies to respond swiftly to changing market conditions. This mobility and adaptability make FLNG a cost-effective and strategic choice for gas production and export, encouraging investments in this technology.
Technological Advancements
Continuous advancements in FLNG technology are propelling the market forward. Innovations in liquefaction processes, vessel design, and safety systems enhance the efficiency and reliability of FLNG operations. These technological improvements not only reduce operational costs but also increase the lifespan and performance of FLNG units. As technology evolves, the feasibility and attractiveness of FLNG projects improve, driving further growth and development in the market.
Supportive Regulatory Frameworks
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing policies that favor the development and use of FLNG technology. Financial incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies, along with regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions, are encouraging the adoption of FLNG. These supportive measures help mitigate the high upfront costs associated with FLNG projects and create a favorable environment for industry growth. Regulatory support plays a crucial role in driving the FLNG market as it helps overcome economic barriers and promotes sustainable energy solutions.
Environmental Sustainability
FLNG technology contributes to environmental sustainability by providing a cleaner energy source and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing stranded gas reserves that would otherwise remain untapped, FLNG helps minimize environmental impact. Moreover, FLNG projects often incorporate advanced environmental controls and carbon capture technologies, further enhancing their green credentials. The focus on sustainability aligns with global efforts to combat climate change, making FLNG an attractive option for environmentally conscious stakeholders.
Economic Development and Job Creation
The development of FLNG projects can stimulate local economies by creating jobs and attracting investments. Building and operating FLNG facilities require a range of skills and expertise, generating employment opportunities in engineering, construction, and operations. Additionally, the export of liquefied natural gas contributes to national revenue and economic growth. These economic benefits, combined with the strategic importance of energy security, drive government and private sector investments in the FLNG market.
Restraints for the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market
High Initial Costs
One of the biggest restraints in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) market is the high initial investment required. Building FLNG vessels and infrastructure is incredibly expensive, often reaching billions of dollars. These high upfront costs can deter potential investors and companies, especially when compared to traditional onshore LNG facilities. The financial risk associated with such a significant investment is a major hurdle, as it requires substantial capital and long-term financial commitment.
Technological Challenges
Another key restraint is the technological complexity involved in FLNG operations. The technology required to extract, liquefy, and store natural gas on a floating vessel is highly sophisticated. This includes advanced engineering for stability in rough sea conditions and specialized equipment for gas processing and storage. These technological demands can lead to higher operational risks and potential failures, which further complicate the adoption of FLNG solutions. Continuous advancements and maintenance of such technology are necessary, but they come with a high cost and require specialized expertise.
Regulatory and Environmental Concerns
Regulatory and environmental challenges also play a significant role in restraining the FLNG market. Different countries have varied regulatory frameworks for offshore operations, which can create compliance challenges for FLNG projects. Moreover, environmental concerns, such as the impact on marine ecosystems and the risk of spills, add to the complexity of gaining approvals and maintaining operations. Stricter regulations and environmental scrutiny can delay projects and increase costs, making FLNG less attractive compared to onshore alternatives.
Market Competition
The FLNG market faces stiff competition from other energy sources and LNG infrastructure options. Onshore LNG terminals, which are well-established and often more cost-effective, pose significant competition. Additionally, renewable energy sources are becoming more viable and attractive, reducing the demand for natural gas. This competitive landscape forces FLNG projects to justify their higher costs and technological complexities against more traditional and emerging energy solutions.
Economic Volatility
Economic volatility, such as fluctuations in global oil and gas prices, can significantly impact the viability of FLNG projects. Since these projects require long-term investments, any downturn in the energy market can lead to financial losses and reduced profitability. The economic uncertainty makes it challenging to secure financing and can deter investors from committing to FLNG ventures. This economic sensitivity adds another layer of risk to the already complex FLNG market.
Opportunity in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market
Expanding Energy Access
The Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) market offers significant opportunities by enhancing access to offshore gas reserves. This technology allows energy companies to tap into natural gas sources that were previously inaccessible or too costly to develop with traditional methods. By enabling the development of these offshore reserves, FLNG expands the availability of natural gas, which is a cleaner energy source compared to coal and oil. This expansion helps meet the growing global demand for energy, especially in regions with increasing consumption needs.
Cost-Efficiency
FLNG projects present a cost-effective solution compared to traditional onshore liquefaction facilities. By eliminating the need for extensive onshore infrastructure, FLNG reduces both capital and operational expenditures. The mobility and flexibility of FLNG units further enhance their cost-effectiveness. They can be moved to different gas fields as needed, optimizing production and reducing the financial risks associated with permanent installations. This adaptability allows companies to respond quickly to changes in market conditions and gas supply.
Environmental Benefits
Environmental sustainability is another significant opportunity presented by the FLNG market. FLNG technology can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing and utilizing gas that would otherwise be flared or vented. The use of advanced environmental controls on FLNG units further mitigates their environmental impact. Moreover, by enabling the use of natural gas, which burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, FLNG contributes to the global transition towards more sustainable energy sources.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
FLNG projects stimulate economic development and job creation in the regions where they are deployed. These projects require a skilled workforce for construction, operation, and maintenance, thereby creating employment opportunities. Additionally, the development of FLNG infrastructure attracts investments and generates revenue through gas exports. This economic boost can be particularly beneficial for developing countries with significant offshore gas reserves.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing advancements in FLNG technology open new avenues for growth in the market. Innovations in liquefaction processes, vessel design, and safety systems enhance the efficiency and reliability of FLNG operations. The integration of digital technologies and automation further improves operational performance and reduces costs. These technological improvements make FLNG an increasingly viable and attractive option for natural gas extraction and processing.
Strategic Partnerships
Strategic collaborations between energy companies, engineering firms, and vessel operators are crucial for the successful implementation of FLNG projects. These partnerships combine expertise, resources, and technology, facilitating the development of efficient and cost-effective FLNG solutions. Such collaborations also help in sharing risks and addressing the technical complexities associated with FLNG operations, ensuring the smooth execution and sustainability of these projects .
Trends for the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market
Technological Advancements
The FLNG market is seeing significant technological advancements. Innovations such as improved liquefaction methods and more efficient storage solutions are driving the market forward. These advancements help in making FLNG projects more economically viable and operationally efficient, reducing costs and increasing profitability. The integration of renewable energy sources into FLNG operations is also a notable trend, aligning the industry with global sustainability goals.
Modular and Scalable Designs
FLNG facilities are increasingly adopting modular and scalable designs. This flexibility allows for better management of project risks and uncertainties associated with gas field characteristics. Modular designs enable quicker and more cost-effective deployment of FLNG units, facilitating the monetization of smaller or more remote gas reserves that would otherwise be uneconomical to develop.
Environmental and Regulatory Focus
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are shaping the FLNG market. There is a growing emphasis on reducing the environmental footprint of FLNG operations. Innovations aimed at minimizing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency are becoming standard. Additionally, compliance with international environmental regulations is crucial, driving the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices in the industry.
Market Expansion Opportunities
The FLNG market is expanding geographically, with new opportunities emerging in regions with untapped offshore gas reserves. Countries in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and South America are investing in FLNG projects to capitalize on their natural gas resources. This geographical diversification is crucial for the growth of the FLNG market, providing new avenues for development and investment.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaborations and partnerships among energy companies, engineering firms, and technology providers are becoming more common in the FLNG market. These strategic alliances are essential for sharing expertise, reducing costs, and accelerating project timelines. Joint ventures and partnerships help mitigate the high risks and significant capital investments associated with FLNG projects.
Impact of Geopolitical and Economic Factors
Geopolitical and economic factors significantly influence the FLNG market. Fluctuations in global energy prices, trade policies, and political stability in key regions can impact the viability and attractiveness of FLNG projects. Companies need to adopt strategic risk management approaches to navigate these uncertainties and ensure the long-term success of their FLNG investments .
Segments Covered in the Report
By Technology
o LNG FPSO
o FSRU
o Others
By Capacity
o Small/Mid-Scale
o Large Scale
o Others
By End-Use
o Power Generation
o Industrial
o Others
Segment Analysis
By Technology Analysis
Based on technology, the floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) market has been divided into LNG FPSO, FSRU, and Others. The biggest market share for floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) in 2023 is held by the FSRU sector. Some of the factors propelling the growth of the FSRU market are the expanding demand for natural gas production, the expansion of global LNG commerce, and the growing demand for LNG imports from the power plant and automobile industries.
Transferring and shipping LNG (liquefied natural gas) across the ocean requires a floating storage regasification unit or FSRU. As a result, FSRUs are a unique class of ship utilized in LNG transfer. LNG is an excellent fuel substitute that is efficient and kind to the environment, but it's vital to recognize the difficulties in moving it. Errors in this procedure have the potential to cost lives and fuel, not to mention worsen the condition of the ocean.
The LNG fuel is delivered to the needed location in a semi-cooled, slushy form at -160 ˦C. The gas must be heated back up to its initial gaseous condition before being pumped into its storage systems. The warming procedure is costly and requires a lot of time. A floating storage unit with a reliquefication plant has been designed as a method to deal with this problem.
Based on the design they use, FSRU vessels can be categorized as either ships or offshore installations. When the FSRU unit is mounted within the ship, its design resembles that of other LNG ships that are engaged in LNG trading operations, regularly dry dock, and adhere to all applicable international marine safety regulations.
One of the main benefits of this setup is that the gasoline may be heated and liquefied inside the ship, saving the semi-frozen slushy fuel from needing to be unloaded. Continuous transference of the LNG cargo from LNG boats would ensure that there is no storage depletion at all since the renovated Floating Storage Regasification Unit (FSRU) would also be able to provide storing feasibilities of LNG.
The Floating Storage and Regasification Unit presents novel prospects for LNG importation for nations. FSRU can be moored at sea or to a docking facility. Compared to an onshore system, it can be implemented more quickly and at a lower cost. A floating regasification solution is typically less expensive than a conventional land-based one. FSRUs bridge the access gap to greener energy by enabling nations to move away from coal and liquid fuels.
By Capacity Analysis
The Floating LNG Market is divided into three categories based on capacity: small/mid-scale, large-scale, and others. Throughout the floated liquefied natural gas (FLNG) market forecast period, the large-scale category is expected to continue to dominate with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9%. Large-scale FLNG projects are calculated risks that have a big effect on the LNG market worldwide. These entail large expenditures, a vast infrastructure, and state-of-the-art technology to supply liquefied natural gas in a stable and substantial amount to meet the world's energy needs. To ensure sustainable and responsible practices, economic, environmental, and social concerns must be carefully considered during the construction and operation of such initiatives. These elements support the expansion of the floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) market.
By End-Use Analysis
In 2023, the segment with the most revenue share was power generation. For generating electricity, liquefied natural gas is an affordable, low-carbon fuel source. For more affordable power generation, a lot of power-producing companies throughout the world are obtaining LNG. Additionally, several nations banned the import of coal, which has expedited the expansion of this market. The European Union (EU) banned Russian coal imports beginning in August 2022, according to the World Bank. Furthermore, gas turbines are an affordable way to produce energy, which is why many power generation firms have installed gas turbine units to produce electricity. The segment is growing more quickly as a result of these factors.
Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific area is the primary user of natural gas, which is fueling the need for FLNG projects. Major offshore gas reserves in nations like Australia, Malaysia, and Indonesia are a major factor driving FLNG advancements. Significant offshore gas reserves are found in the Middle East and Africa, especially in nations like Tanzania and Mozambique. This region's FLNG projects present chances to address the region's expanding energy needs while also monetizing these resources.
Additionally, the gas market in Europe is well-established, but there are still chances for FLNG projects in areas like the North Sea and the Mediterranean. Additionally, Europe's efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and switch to cleaner energy sources are helping to advance FLNG technology.
Competitive Analysis
The market for floating LNG is highly concentrated, with a few number of businesses controlling the majority of the revenue generated by the product. Big players are using a variety of tactics, including contracts, investments, mergers and acquisitions, and strategic agreements.
Recent Developments
January 2023: The floating LNG regasification unit in Lubmin, Germany was put into service by TotalEnergies SE, an integrated energy and petrochemical firm based in France. The new machine can regasify five billion cubic meters of gas yearly. This project will assist Germany's primary LNG suppliers and contribute to the floating storage and regasification unit (FSRU). The development of LNG will be greatly aided by this strategic move.
November 2022: An order for USD 496.4 million was placed with Samsung Heavy Industries to build a liquefied natural gas carrier. Samsung Heavy Industries is actively engaged in the FLNG industry and is investigating various prospects from the energy, oil, and gas, as well as maritime industries. New units being built by Samsung Heavy Industries are being built with consideration for the environment. Throughout the projection period, new orders for floating natural gas vessels are anticipated as a result of this new strategy initiative, which will also aid in income generation.
Key Market Players in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Market
o ABB Ltd.
o Woodside Energy Group Ltd
o Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS)
o Hoegh LNG
o EXMAR
o Excelerate Energy Inc.
o Golar LNG Limited
o BASF SE
o Mitsui O.S.K.Lines
o Other Key Players
|
Report Features |
Description |
|
Market Size 2023 |
USD 22.9 Billion |
|
Market Size 2033 |
USD 55.7 Billion |
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
8.8% (2023-2033) |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Market Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
|
Historical Data |
2019-2022 |
|
Market Forecast Units |
Value (USD Billion) |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, Capacity, End-Use, and Region |
|
Geographies Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World |
|
Countries Covered |
The U.S., Canada, Germany, France, U.K, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Brazil |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
ABB Ltd., Woodside Energy Group Ltd, Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Hoegh LNG, EXMAR, Excelerate Energy Inc., Shell plc, Golar LNG Limited, BASF SE, Mitsui O.S.K.Lines, Other Key Players |
|
Key Market Opportunities |
Expanding Energy Access |
|
Key Market Dynamics |
Increasing Demand for Natural Gas |
📘 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What would be the forecast period in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market?
Answer: The forecast period in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market report is 2024-2033.
2. How much is the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market in 2023?
Answer: The Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market size was valued at USD 0.4 Billion in 2023.
3. Who are the key players in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market?
Answer: ABB Ltd., Woodside Energy Group Ltd, Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Hoegh LNG, EXMAR, Excelerate Energy Inc., Shell plc, Golar LNG Limited, BASF SE, Mitsui O.S.K.Lines, Other Key Players
4. What is the growth rate of the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market?
Answer: Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Market is growing at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period, from 2023 to 2033.

🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
- Accurate & Verified Data:Our insights are trusted by global brands and Fortune 500 companies.
- Complete Transparency:No hidden fees, locked content, or misleading claims — ever.
- 24/7 Analyst Support:Our expert team is always available to help you make smarter decisions.
- Instant Savings:Enjoy a flat $1000 OFF on every report.
- Fast & Reliable Delivery:Get your report delivered within 5 working days, guaranteed.
- Tailored Insights:Customized research that fits your industry and specific goals.



