
🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
At Infinity Market Research, we dont just deliver data — we deliver clarity, confidence, and competitive edge.
In a world driven by insights, we help businesses unlock the infinite potential of informed decisions.
Here why global brands, startups, and decision-makers choose us:
Industry-Centric Expertise
With deep domain knowledge across sectors — from healthcare and technology to manufacturing and consumer goods — our team delivers insights that matter.
Custom Research, Not Cookie-Cutter Reports
Every business is unique, and so are its challenges. Thats why we tailor our research to your specific goals, offering solutions that are actionable, relevant, and reliable.
Data You Can Trust
Our research methodology is rigorous, transparent, and validated at every step. We believe in delivering not just numbers, but numbers that drive real impact.
Client-Centric Approach
Your success is our priority. From first contact to final delivery, our team is responsive, collaborative, and committed to your goals — because you re more than a client; you re a partner.
Recent Reports
Obesity Management Market
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Global Industry Analysis and Forecast (2024-2032) By Type, (Cadmium Telluride, Copper Indium Gallium Di selenide, Amorphous Thin-Film Silicon. By Installation (On-Grid, Off-Grid) By End User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Utility) and Region
Mar 2025
Energy and Power
Pages: 138
ID: IMR1888
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Synopsis
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market research report acquired the significant revenue of XX Billion in 2023 and expected to be worth around USD XX Billion by 2032 with the CAGR of XX% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2032.
Usually few micrometers thick, thin layers of semiconductor materials typically used in photovoltaic technology characterize thin-film solar cells, a form of photovoltaic technology used to collect sunlight and generate electricity. Built on flexible or stiff substrates glass, plastic, metal, or another material these cells allow lightweight and adaptable uses in the home, business, and industrial sectors. Each of thin-film technologies amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) offers unique benefits including reduced material use, improved performance in low-light settings, and surface-oriented adaptation. Their increasing relevance in sustainable energy solutions is shown by their capacity to be included into automobiles, construction materials, and portable tools.
Driven by developments in photovoltaic technology, increased demand for renewable energy sources, and a growing focus on sustainability, the thin-film solar cell market is seeing strong expansion. Renowned for its flexible construction and light weight, thin-film solar cells present a good substitute for conventional silicon-based solar cells. These qualities allow its use in residential, business, and industrial environments among other spheres. Government regulations supporting sustainable energy and global efforts to lower carbon footprints help the market by so fostering the acceptance of these creative solar solutions. Attractiveness of the market also stems from cost benefits in manufacturing relative to crystalline silicon cells.
The efficiency and scalability of technological developments in thin-film solar cell manufacture including cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon (a-Si) technologies are widening. Thin-film solar cells are favored for large-scale solar projects since innovations in tandem cell designs and integration with other renewable technologies have improved energy conversion rates. Moreover, continuous research and development initiatives help to solve efficiency constraints, thereby increasing their acceptance in markets with difficult climate conditions.
Driven by large expenditures in renewable energy infrastructure and growing electricity consumption, the Asia-Pacific region rules the thin-film solar cell market. Thanks to their supporting policies and great manufacturing capacity, nations such China, Japan, and India are making leading contributions. Strong regulations, financial incentives, and rising acceptance of solar technologies in both residential and commercial sectors help North America and Europe also experience significant expansion. Rising energy access programs and lowering thin-film solar installation costs are driving promise in emerging countries in Latin America and Africa.
Notwithstanding its expansion path, the market suffers difficulties including competition from crystalline silicon technologies and worries about environmental and health effects of some materials used in thin-film manufacturing. Increasing investments in recycling technologies and sustainable materials, however, help to solve these problems. Over the next ten years, the thin-film solar cell industry is expected to grow steadily thanks to ongoing innovation, strategic alliances, and widening uses in industries including transportation and portable devices.
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Trend Analysis
Trend
Lightweight and Flexible Design Driving Adoption
Because of its lightweight and flexible form, thin-film solar cells which are perfect for many uses including building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), portable devices, and large-scale utility projects are fast becoming more and more important. Thin-film cells provide more flexibility than typical rigid solar panels since they may be easily placed on unusual surfaces including curved rooftops, facades, and even portable buildings. Their special capacity to remain efficient at low light levels and high temperatures increases their applicability especially in areas with varying sunlight or severe storms. These benefits are boosting their acceptance in the home as well as the business sectors in line with the increasing focus on including renewable energy sources into regular infrastructure.
Furthermore boosting investments in thin-film solar technologies is the worldwide turn toward renewable energy as a sustainable substitute for fossil fuels. Through subsidies, tax breaks, and money for research and development, governments and businesses are helping this shift ever more. This has resulted in ongoing thin-film material research that improves energy conversion efficiencies and lowers manufacturing costs. These solar cells are thus becoming more easily available and aesthetically pleasing to a larger audience, so reinforcing their part in the worldwide clean energy movement.
Opportunity
Advancements in Thin-Film Solar Cell Technology
Thin-film solar cells have become ever more cost-effective and efficient as solar technology develops, offering significant chances for broad use in many different fields. Their versatility enables incorporation into building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), automotive, and consumer electronics as well as other uses. Because thin-film solar cells may be easily included into current infrastructure and goods, this adaptability creates fresh opportunities for market expansion. Moreover, their adaptability to lightweight materials and flexible surfaces makes them a desirable choice for sectors trying to lower energy usage and support environmentally friendly solutions. The increasing need for environmentally friendly and energy-efficient goods in both home and business sectors improves the whole possibilities of thin-film solar technology.
Furthermore, compared to conventional crystalline silicon solar cells, thin-film solar cells provide a major benefit in terms of manufacturing expenses. For large-scale solar projects, especially in areas with lots of sunlight and reasonably priced land, their cost-effectiveness appeals. Thin-film solar technology's scalability helps it to be a perfect answer for both utility-scale solar farms and smaller off-grid installations as the world's need for renewable energy increases. Thin-film solar cells are positioned for rising acceptance in the energy industry based on their economic advantages, adaptability, and alignment with sustainability goals, thereby helping to drive the change toward a more sustainable and dispersed energy future.
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Segment Analysis
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Segmented on the basis of By Type, By Installation, By End User.
By Type
o Cadmium Telluride
o Copper Indium Gallium Di selenide
o Amorphous Thin-Film Silicon
By Installation
o On-Grid
o Off-Grid
By End Use
o Residential
o Commercial
o Industrial and Utility
By Region
o North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
o Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe)
o Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe)
o Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New-Zealand, Rest of APAC)
o Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa)
o South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
By Type, Cadmium Telluride segment is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period
Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) is one of the leading thin-film solar technologies, widely recognized for its cost-effectiveness and relatively high efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. This technology utilizes a thin layer of cadmium telluride as the semiconductor, which performs optimally in regions with abundant sunlight. One of the main advantages of CdTe is its low production cost compared to traditional silicon-based solar cells, making it an attractive choice for large-scale commercial and utility applications. Its efficiency has improved significantly over the years, and with advancements in manufacturing processes, CdTe panels are becoming increasingly competitive in the solar market, particularly in price-sensitive markets where affordability is key.
Despite its advantages, CdTe technology faces challenges regarding environmental concerns. The primary issue is the toxicity of cadmium, a heavy metal used in the production of the solar panels. While the panels are safe to use during their lifecycle, proper disposal and recycling of CdTe panels at the end of their life cycle is a significant concern. The potential environmental impact of cadmium contamination may limit the widespread adoption of CdTe technology in some regions, particularly those with stricter environmental regulations. However, ongoing research into recycling methods and alternative materials may help mitigate these concerns, allowing for the continued growth of CdTe solar technology.
By End User, Commercial segment expected to held the largest share
Commercial solar installations have become a key solution for businesses aiming to reduce their energy costs while enhancing their sustainability efforts. These systems are typically larger than residential installations and are designed to serve the energy needs of small to large corporate buildings. Commercial solar systems are often on-grid, enabling businesses to benefit from net metering, which credits them for excess energy they generate and feed back into the grid. This can significantly reduce electricity bills and provide businesses with a reliable return on investment. Due to their larger scale, these installations require substantial capital investment, but the long-term savings in energy costs and operational efficiencies can outweigh the initial expenses.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important goal for organizations, the demand for commercial solar solutions has surged. Businesses are keen to improve their environmental impact while lowering operational costs, and solar energy provides a practical way to achieve both objectives. In addition, commercial solar installations benefit from various incentives, such as tax rebates, grants, and credits, which help offset the installation costs. These financial incentives, along with the growing pressure to adopt green practices, make commercial solar systems an attractive option for companies aiming to enhance their environmental credentials while also achieving cost savings. With advancements in solar technology and favorable policy environments, the adoption of commercial solar energy is expected to continue growing in the coming years.
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Regional Insights
North America is Expected to Dominate the Market Over the Forecast period
Thanks in great part to significant expenditures in renewable energy infrastructure, the thin-film solar cell business has grown rather rapidly in North America, especially in the United States and Canada. Accelerating the acceptance of thin-film solar technologies has been much aided by government incentives ranging from tax credits to grants to subsidies. These rules not only lower the initial capital outlay for the commercial and residential sectors but also provide pleasing surroundings for initiatives using sustainable energy. Moreover, growing knowledge of environmental sustainability and the necessity of energy independence has motivated consumers and companies to investigate solar energy substitutes; thin-film solar cells have become a common choice because of their affordability and capacity to fit into many kinds of buildings.
Major firms in the solar energy sector as well as research facilities aimed at developing thin-film technology have greatly helped to propel the market forward. Thin-film solar cells' cheaper installation costs and adaptability make them particularly appropriate for homes and businesses where space and aesthetic concerns rule. In cities, where rooftops are sometimes constrained in space, thin-film solar technology presents a workable and effective answer. Supported by both technology developments and favorable governmental frameworks, the thin-film solar cell market in North America is likely to expand at an accelerated rate as the area keeps giving sustainable energy projects top priority.
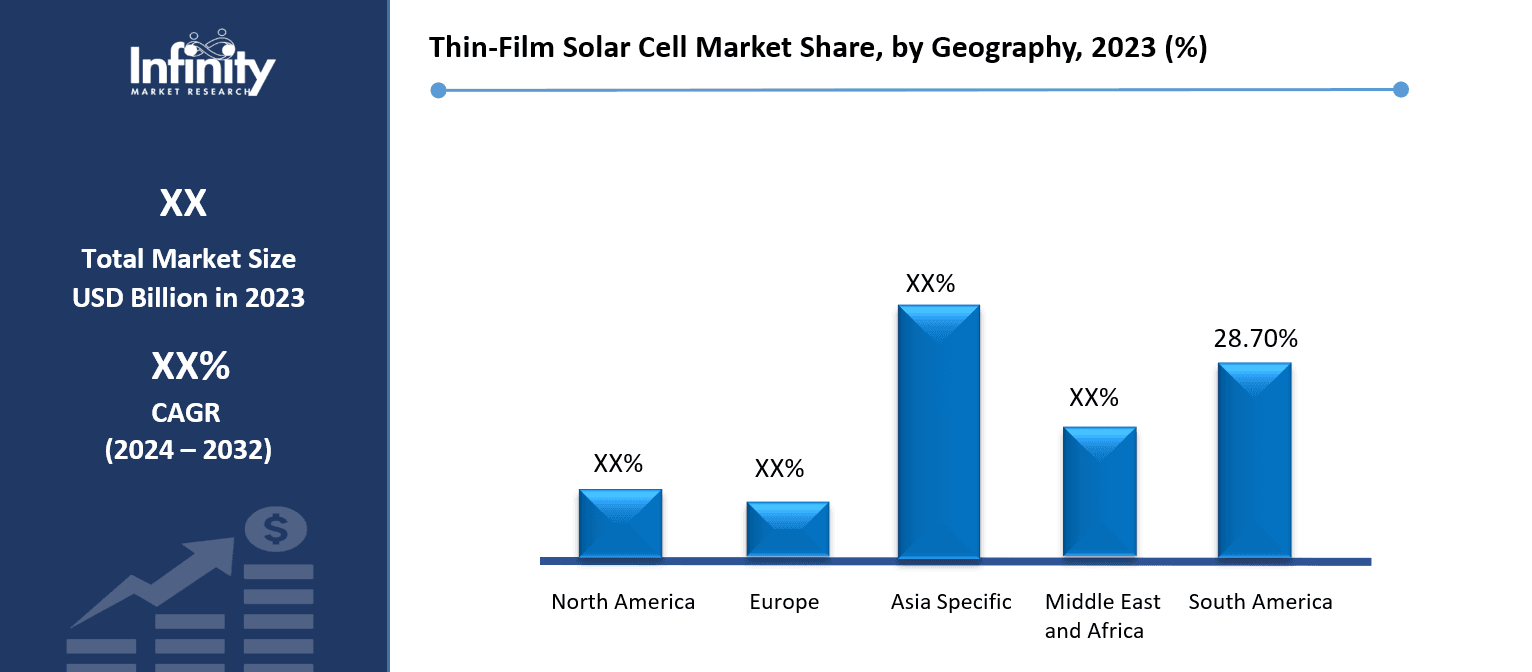
Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Share, by Geography, 2023 (%)
Active Key Players in the Thin-Film Solar Cell Market
o Greatcell (Australia)
o Exeger Operations AB (Sweden)
o Fujikura Europe Ltd. (U.K.)
o G24 Power Ltd. (U.K.)
o Konica Minolta Sensing Europe B.V. (Netherlands)
o Merck KGaA (Germany)
o Oxford PV (U.K.)
o Peccell Technologies, Inc. (Japan)
o Sharp Corporation (Japan)
o Solaronix SA (Switzerland)
o Sony Corporation (Japan)
o Ricoh (Japan)
o First Solar. (US)
o SunPower Corporation (U.S.)
o Suniva Inc (U.S.)
o Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd. (India)
o SHARP CORPORATION (Japan)
o ALPS Technology Inc. (U.S.)
o Solaris Technology Industry, Inc. (India)
o GREEN BRILLIANCE RENEWABLE ENERGY LLP (India)
o Trina Solar (China)
o Other key Players
Global Thin-Film Solar Cell Market Scope
|
Global Thin-Film Solar Cell Market | |||
|
Base Year: |
2023 |
Forecast Period: |
2024-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2017 to 2023 |
Market Size in 2023: |
USD XX Billion |
|
Forecast Period 2024-32 CAGR: |
XX% |
Market Size in 2032: |
USD XX Billion |
|
|
By Type |
· Cadmium Telluride · Copper Indium Gallium Di selenide · Amorphous Thin-Film Silicon | |
|
By Installation |
· On-Grid · Off-Grid | ||
|
By End User |
· Residential · Commercial · Industrial and Utility | ||
|
By Region |
· North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico) · Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Rest of Eastern Europe) · Western Europe (Germany, UK, France, Netherlands, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Western Europe) · Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, The Philippines, Australia, New-Zealand, Rest of APAC) · Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Bahrain, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE, Israel, South Africa) · South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA) | ||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
· Transition to Sustainable Energy Solutions | ||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
· High Initial Investment for Manufacturing Facilities | ||
|
Key Opportunities: |
· Advancements in Thin-Film Solar Cell Technology | ||
|
Companies Covered in the report: |
· Greatcell (Australia), Exeger Operations AB (Sweden), Fujikura Europe Ltd. (U.K.), G24 Power Ltd. (U.K.), Konica Minolta Sensing Europe B.V. (Netherlands), Merck KGaA (Germany), Oxford PV (U.K.), Peccell Technologies, Inc. (Japan), Sharp Corporation (Japan), Solaronix SA (Switzerland), Sony Corporation (Japan), Ricoh (Japan), First Solar. (US), SunPower Corporation (U.S.), Suniva Inc (U.S.), Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd. (India), SHARP CORPORATION (Japan), ALPS Technology Inc. (U.S.), Solaris Technology Industry, Inc. (India), GREEN BRILLIANCE RENEWABLE ENERGY LLP (India), Trina Solar (China) and Other Major Players. | ||
📘 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What would be the forecast period in the Thin-Film Solar Cell Market research report?
Answer: The forecast period in the Market research report is 2024-2032.
2. Who are the key players in the Thin-Film Solar Cell Market?
Answer: Greatcell (Australia), Exeger Operations AB (Sweden), Fujikura Europe Ltd. (U.K.), G24 Power Ltd. (U.K.), Konica Minolta Sensing Europe B.V. (Netherlands), Merck KGaA (Germany), Oxford PV (U.K.), Peccell Technologies, Inc. (Japan), Sharp Corporation (Japan), Solaronix SA (Switzerland), Sony Corporation (Japan), Ricoh (Japan), First Solar. (US), SunPower Corporation (U.S.), Suniva Inc (U.S.), Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd. (India), SHARP CORPORATION (Japan), ALPS Technology Inc. (U.S.), Solaris Technology Industry, Inc. (India), GREEN BRILLIANCE RENEWABLE ENERGY LLP (India), Trina Solar (China) and Other Major Players.
3. What are the segments of the Thin-Film Solar Cell Market?
Answer: The Thin-Film Solar Cell Market is segmented into By Type, By Installation, By End User and region. By Type, the market is categorized into Cadmium Telluride, Copper Indium Gallium Di selenide, Amorphous Thin-Film Silicon. By Installation, the market is categorized into On-Grid, Off-Grid. By End User, the market is categorized into Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Utility. By region, it is analyzed across North America (U.S.; Canada; Mexico), Eastern Europe (Bulgaria; The Czech Republic; Hungary; Poland; Romania; Rest of Eastern Europe), Western Europe (Germany; UK; France; Netherlands; Italy; Russia; Spain; Rest of Western Europe), Asia-Pacific (China; India; Japan; Southeast Asia, etc.), South America (Brazil; Argentina, etc.), Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia; South Africa, etc.).
4. What is the Thin-Film Solar Cell Market?
Answer: Usually few micrometers thick, thin layers of semiconductor materials—typically used in photovoltaic technology—characterize thin-film solar cells, a form of photovoltaic technology used to collect sunlight and generate electricity. Built on flexible or stiff substrates—glass, plastic, metal, or another material—these cells allow lightweight and adaptable uses in the home, business, and industrial sectors. Each of thin-film technologies—amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)—offers unique benefits including reduced material use, improved performance in low-light settings, and surface-oriented adaptation. Their increasing relevance in sustainable energy solutions is shown by their capacity to be included into automobiles, construction materials, and portable tools.

🔐 Secure Payment Guaranteed
Safe checkout with trusted global payment methods.
🌟 Why Choose Infinity Market Research?
- Accurate & Verified Data:Our insights are trusted by global brands and Fortune 500 companies.
- Complete Transparency:No hidden fees, locked content, or misleading claims — ever.
- 24/7 Analyst Support:Our expert team is always available to help you make smarter decisions.
- Instant Savings:Enjoy a flat $1000 OFF on every report.
- Fast & Reliable Delivery:Get your report delivered within 5 working days, guaranteed.
- Tailored Insights:Customized research that fits your industry and specific goals.



